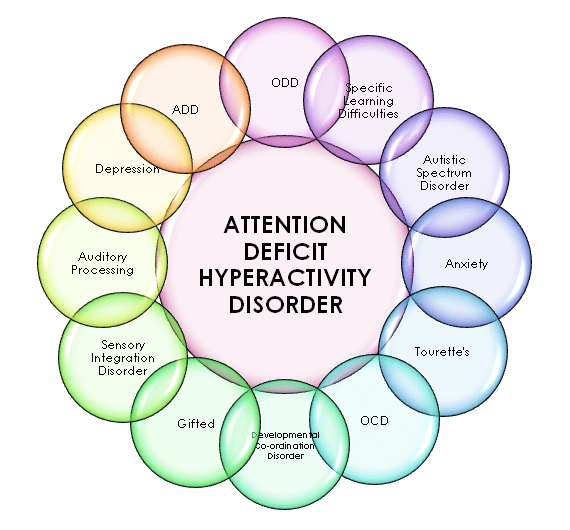
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental condition characterized by difficulty paying attention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity.
ADHD is one of the most common neurodevelopmental disorders of childhood. It is estimated to affect 5-10% of school-aged children worldwide. ADHD can range in severity from mild to severe, and it can have a significant impact on a child's academic, social, and emotional development.
The exact cause of ADHD is unknown, but it is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. ADHD is often treated with medication, therapy, or a combination of both.
With proper treatment, children with ADHD can learn to manage their symptoms and live happy, fulfilling lives.
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
ADHD is a neurodevelopmental condition characterized by difficulty paying attention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity. It is one of the most common neurodevelopmental disorders of childhood, affecting 5-10% of school-aged children worldwide.
- Inattention
- Impulsivity
- Hyperactivity
- Diagnosis
- Treatment
- Prognosis
- Support
These key aspects of ADHD provide a comprehensive overview of the condition, from its symptoms and diagnosis to its treatment and prognosis. It is important to understand these aspects in order to effectively support children with ADHD and help them reach their full potential.
1. Inattention
Inattention is one of the core symptoms of ADHD. It is characterized by difficulty paying attention to tasks, staying focused, and following instructions. Children with ADHD may also have difficulty staying organized, remembering things, and completing tasks on time.
Inattention can have a significant impact on a child's academic, social, and emotional development. Children with ADHD may struggle in school, have difficulty making and keeping friends, and may be more likely to experience anxiety and depression.
There are a number of things that can be done to help children with inattention. These include:
- Providing a structured environment with clear rules and expectations
- Breaking down tasks into smaller steps
- Using visual aids, such as charts and graphs
- Offering positive reinforcement for good behavior
- Working with a therapist or counselor to develop coping mechanisms
With proper support, children with inattention can learn to manage their symptoms and succeed in school and in life.
2. Impulsivity
Impulsivity is another core symptom of ADHD. It is characterized by acting without thinking, taking risks, and having difficulty waiting for rewards. Children with ADHD may also be more likely to interrupt others, blurt out answers, and have difficulty controlling their emotions.
Impulsivity can have a significant impact on a child's academic, social, and emotional development. Children with ADHD may struggle in school, have difficulty making and keeping friends, and may be more likely to experience accidents and injuries.
There are a number of things that can be done to help children with impulsivity. These include:
- Teaching children to think before they act
- Helping children to learn how to wait for rewards
- Providing children with opportunities to practice self-control
- Working with a therapist or counselor to develop coping mechanisms
With proper support, children with impulsivity can learn to manage their symptoms and succeed in school and in life.
3. Hyperactivity
Hyperactivity is a core symptom of ADHD that is characterized by excessive fidgeting, restlessness, and difficulty sitting still. Children with ADHD may also be more likely to run, jump, and climb, even in inappropriate situations.
- Physical Hyperactivity
Physical hyperactivity is the most common type of hyperactivity. It can manifest in a variety of ways, such as fidgeting, squirming, running, jumping, and climbing. Children with physical hyperactivity may also have difficulty sitting still, especially in quiet or structured settings.
- Verbal Hyperactivity
Verbal hyperactivity is characterized by excessive talking, interrupting, and blurting out answers. Children with verbal hyperactivity may also have difficulty taking turns in conversations and waiting their turn to speak. They may also be more likely to make loud noises and sing or hum to themselves.
- Cognitive Hyperactivity
Cognitive hyperactivity is characterized by difficulty paying attention, staying focused, and completing tasks. Children with cognitive hyperactivity may also be more likely to daydream, get distracted easily, and make careless mistakes. They may also have difficulty following instructions and remembering things.
- Emotional Hyperactivity
Emotional hyperactivity is characterized by difficulty controlling emotions. Children with emotional hyperactivity may be more likely to have temper tantrums, cry easily, and overreact to situations. They may also be more likely to experience anxiety and depression.
Hyperactivity can have a significant impact on a child's academic, social, and emotional development. Children with hyperactivity may struggle in school, have difficulty making and keeping friends, and may be more likely to experience accidents and injuries. However, with proper support, children with hyperactivity can learn to manage their symptoms and succeed in school and in life.
4. Diagnosis
An accurate diagnosis is essential for children with ADHD. A proper diagnosis can help to rule out other conditions that may be causing similar symptoms, such as anxiety, depression, or learning disabilities. It can also help to determine the severity of the ADHD symptoms and to develop an appropriate treatment plan.
There is no single test that can diagnose ADHD. Instead, doctors will typically use a combination of methods, including:
- A physical exam
- A review of the child's medical history
- A psychological evaluation
- Observation of the child's behavior
In order to be diagnosed with ADHD, a child must meet certain criteria, including:
- Having at least six symptoms of inattention or hyperactivity-impulsivity that have been present for at least six months
- Having symptoms that are present in two or more settings, such as at home and at school
- Having symptoms that interfere with the child's academic, social, or occupational functioning
It is important to note that ADHD is a complex condition that can vary in severity from child to child. There is no one-size-fits-all treatment for ADHD, and the best course of treatment will vary depending on the individual child.
5. Treatment
Treatment for ADHD typically involves a combination of medication, therapy, and behavioral interventions. Medication can help to improve attention and focus, while therapy can help children to learn coping mechanisms and strategies for managing their symptoms. Behavioral interventions can help to improve behavior and social skills.
There is no one-size-fits-all treatment for ADHD, and the best course of treatment will vary depending on the individual child. However, with proper treatment, children with ADHD can learn to manage their symptoms and succeed in school and in life.
One of the most important aspects of ADHD treatment is early diagnosis and intervention. Early diagnosis can help to prevent the development of secondary problems, such as anxiety, depression, and substance abuse. Early intervention can also help to improve the child's overall prognosis.
6. Prognosis
The prognosis for children with ADHD varies depending on the severity of their symptoms and the type of treatment they receive. However, with proper treatment, most children with ADHD can learn to manage their symptoms and live happy, fulfilling lives.
Early diagnosis and intervention is essential for a good prognosis. Children who are diagnosed and treated early are more likely to develop coping mechanisms and strategies for managing their symptoms. They are also more likely to avoid the development of secondary problems, such as anxiety, depression, and substance abuse.
There are a number of factors that can affect the prognosis for children with ADHD. These include:
- The severity of the child's symptoms
- The type of treatment the child receives
- The child's response to treatment
- The child's family and social support
Children with ADHD who have a supportive family and social network are more likely to have a good prognosis. They are also more likely to benefit from treatment and to develop coping mechanisms and strategies for managing their symptoms.
Overall, the prognosis for children with ADHD is good. With proper treatment and support, most children with ADHD can learn to manage their symptoms and live happy, fulfilling lives.
7. Support
Support is essential for children with ADHD. It can help them to manage their symptoms, improve their academic performance, and develop positive social skills. There are many different types of support that can be helpful for children with ADHD, including:
- Family support: Parents and other family members can provide emotional support, practical help, and advocacy for children with ADHD.
- School support: Teachers and other school staff can provide academic support, behavioral support, and social support for children with ADHD.
- Community support: There are many community organizations that provide support for children with ADHD and their families. These organizations can offer a variety of services, such as tutoring, social skills groups, and respite care.
Support can make a significant difference in the lives of children with ADHD. It can help them to reach their full potential and to live happy, fulfilling lives.
Here are some examples of how support can help children with ADHD:
- Family support can help children with ADHD to feel loved and accepted. This can help them to develop a positive self-image and to feel more confident in their abilities.
- School support can help children with ADHD to succeed in school. Teachers can provide academic support, such as tutoring and extra help. They can also provide behavioral support, such as positive reinforcement and clear expectations.
- Community support can help children with ADHD to develop social skills and to make friends. Social skills groups can teach children with ADHD how to interact with others and how to resolve conflicts peacefully.
Support is essential for children with ADHD. It can help them to manage their symptoms, improve their academic performance, and develop positive social skills. With the right support, children with ADHD can reach their full potential and live happy, fulfilling lives.
Frequently Asked Questions about ADHD
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental condition characterized by difficulty paying attention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity. It is one of the most common neurodevelopmental disorders of childhood, affecting 5-10% of school-aged children worldwide.
Question 1: What are the symptoms of ADHD?
Answer: The symptoms of ADHD can vary depending on the individual, but they typically include difficulty paying attention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity. Other symptoms may include difficulty following instructions, forgetfulness, disorganization, and difficulty controlling emotions.
Question 2: What causes ADHD?
Answer: The exact cause of ADHD is unknown, but it is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some of the risk factors for ADHD include premature birth, low birth weight, exposure to toxins, and a family history of ADHD.
Question 3: How is ADHD diagnosed?
Answer: ADHD is diagnosed based on a clinical evaluation by a qualified healthcare professional, such as a doctor or psychologist. The evaluation will typically involve a review of the child's symptoms, a physical exam, and a psychological evaluation. There is no single test that can diagnose ADHD.
Question 4: How is ADHD treated?
Answer: ADHD is typically treated with a combination of medication, therapy, and behavioral interventions. Medication can help to improve attention and focus, while therapy can help children to learn coping mechanisms and strategies for managing their symptoms. Behavioral interventions can help to improve behavior and social skills.
Question 5: What is the prognosis for children with ADHD?
Answer: The prognosis for children with ADHD varies depending on the severity of their symptoms and the type of treatment they receive. However, with proper treatment, most children with ADHD can learn to manage their symptoms and live happy, fulfilling lives.
Summary of key takeaways or final thought:
ADHD is a common neurodevelopmental disorder that can affect a child's attention, behavior, and emotions. It is important to understand the symptoms of ADHD and to seek professional help if you suspect that your child may have ADHD. With proper treatment, children with ADHD can learn to manage their symptoms and live happy, fulfilling lives.
Transition to the next article section:
If you have any further questions about ADHD, please consult with a qualified healthcare professional.
Conclusion
ADHD is a common neurodevelopmental disorder that can affect a child's attention, behavior, and emotions. It is important to understand the symptoms of ADHD and to seek professional help if you suspect that your child may have ADHD. With proper treatment, children with ADHD can learn to manage their symptoms and live happy, fulfilling lives.
If you are concerned that your child may have ADHD, please talk to your doctor. Early diagnosis and intervention is essential for a good prognosis. With the right support, children with ADHD can reach their full potential and live happy, fulfilling lives.
You Might Also Like
Latest News About Darryl Hannah And Neil YoungFind Your Celebrity Doppelgnger: Discover The Incredible Celebrity Look Alikes Of DTI
Uncovering Dr. Pol's Current Whereabouts: An Exclusive Revelation
Is Dr. Pol Still Alive Today? The Truth Revealed
The Curious Case Of Molly And Aubreigh: Unraveling The Puzzle
Article Recommendations
- Top Kannada Movies 2024 On Movie Rulzcom
- Renowned Journalist Ted Koppel An Icon In American Broadcasting
- Unveiling The World Of Mkvking A Comprehensive Guide

/adhd-overview-4157275-6982f7abb53c482593834abbc2f3ab73.png)